You may need to learn how to run your website without any help from others. Here is a way to do this.
What you need.
- AWS Account ( you can register for Free Tier account)
Initial Plan
Firstly, I will create an AWS S3 Bucket for uploading the web content. In order to copy the content of the S3 to EC2, I need to create IAM role with s3 full access permission. Then I will launch an AWS EC2 instance and configure the EC2 instance to run my website.
This is very simple. Let's Start.
Steps 1: Create S3 bucket
Go to services and select the S3
Create a bucket
Now click the create button
I have downloaded the basic HTML template website for this blog. you can simply upload your web content to the S3 bucket. Here I have a zip file.
click the newly created bucket and select the web content to upload
Click the upload button
Ok, now we have our web content on the S3 bucket. Let's create an IAM role with s3 full access permission.
Step 2: Create IAM Role
Now go to Security, Identity & Compliance under service and select IAM
Click the create role button
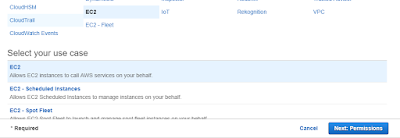
Select EC2 and click on Next:Permission
select the AmazonS3FullAccess
Click the Next:Tag
Then Review and create the role
You have created the role.
Step 3: Create EC2 Instance
Now we need to launch the EC2 instance. Go to Compute under Services and select EC2.
keep step 3 : Configure Instance Detail and Step 4 : Add Storage Step 5: Add Tags as default
Click Review and Launch and then click launch.
Select "create a new key pair" from the drop-down menu and name your key and hit the download key pairs and Launch the Instances. Now go to EC2 and select the instance you just create.
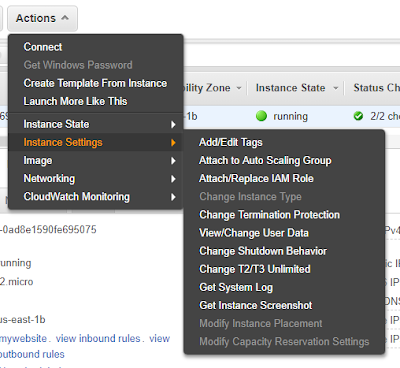
Select the Attach/Replace IAM role under Action
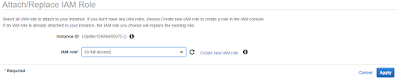
Select the Role that You Created earlier and apply.
copy the IP address and ssh to the EC2 instance using the below command in linux.
ssh -i ~/.ssh/mykey.pem ec2-user@ec2-18-232-95-17.compute-1.amazonaws.com
Now you need to install a server in order to run my website. So I have to install the relevant server using below commands
sudo su yum install httpd -y
Now I need to download the zip file from my s3 bucket.
aws s3 cp s3://harshana-website-demo/myWeb.zip /var/www/html
Unzip the zip file
unzip myWeb.zip
Now, I need to start the httpd server
service httpd start
Ok, we are done.
Open the browser and go to this link http://<ip address>/myWeb/




















Comments
Post a Comment